What Are Dreams ?

A
Thousands of years ago, dreams were seen as messages from the gods, and in many cultures, they are still considered prophetic. In ancient Greece, sick people slept at the temples of Asclepius, the god of medicine, in order to receive dreams that would heal them. Modern dream science really begins at the end of the 19th century with Sigmund Feud, who theorized that dreams were the expression of unconscious desires often stemming from childhood. He believed that exploring these hidden emotions through analysis could help cure mental illness. The Freudian model of psychoanalysis dominated until the 1970s when new research into the chemistry of the brain showed that emotional problems could have biological or chemical roots, as well as environmental ones. In other words, we weren’t sick just because of something our mothers did (or didn’t do), but because of some imbalance that might be cured with medication.
B
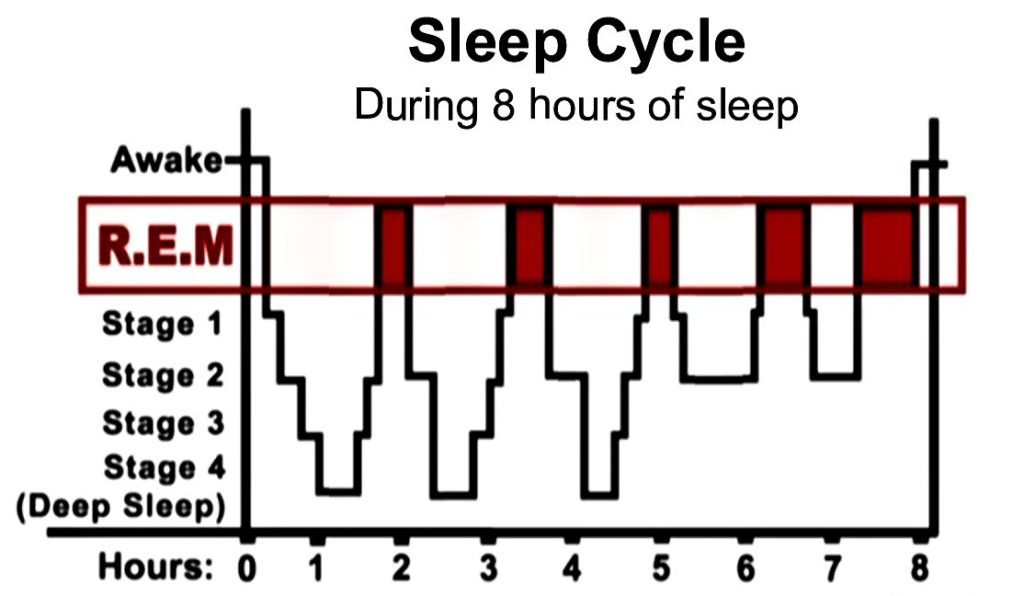
After Freud, the most important event in dream science was the discovery in the early 1950s of a phase of sleep characterized by intense brain activity and rapid eye movement (REM). People awakened in the midst of REM sleep reported vivid dreams, which led researchers to conclude that most dreaming took place during REM. Using the electroencephalograph (EEG), researchers could see that brain activity during REM resembled that of the waking brain. That old them that a lot more was going on at night than anyone had suspected. But what, exactly?
C
Scientists still don’t know for sure, although they have lots of theories. On one side are scientists like Harvard’s Allan Hobson, who believes that dreams are essentially random. In the 1970s, Hobson and his colleague Robert McCarley proposed what they called the “activation-synthesis hypothesis’” which describes how dreams are formed by nerve signals sent out during REM sleep from a small area at the base of the brain called the pons. These signals, the researchers said, activate the images that we call dreams. That put a crimp in dream research; if dreams were meaningless nocturnal firings, what was the point of studying them?
D
Adult humans spend about a quarter of their sleep time in REM, much of it dreaming. During that time, the body is essentially paralyzed but the brain is buzzing. Scientists using PET and fMRI technology to watch the dreaming brain have found that one of the most active areas during REM is the limbic system, which controls our emotions. Much less active is the prefrontal cortex, which is associated with logical thinking. That could explain why dreams in REM sleep often lack a coherent storyline (some researchers have also found that people dream in non-REM sleep as well, although those dreams generally are less vivid.) Another active part of the brain in REM sleep is the anterior cingulate cortex, which detects discrepancies. Eric Nofzinger, director of the Sleep Neuroimaging Program at the University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, thinks that could be why people often figure out thorny problems in their dreams. “As if the brain surveys the internal milieu and tries to figure out what it should be doing, and whether our actions conflict with who we are,” he says.
E
These may seem like vital mental functions, but no one has yet been able to say that REM sleep or dreaming is essential to life or even sanity. MAO inhibitors, an older class of antidepressants, essentially block REM sleep without any detectable effects, although people do get a “REM rebound” – extra REM – if they stop the medication. That’s also true of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) like Prozac, which reduce dreaming by a third to a half. Even permanently losing the ability to dream doesn’t have to be disabling. Israeli researcher Peretz Lavie has been observing a patient named Yuval Chamtzani, who was injured by a fragment of shrapnel that penetrated his brain when he was 19. As a result, he gets no REM sleep and doesn’t remember any dreams. But Lavie says that Chamtzani, now 55, “is probably the most normal person I know and one of the most successful ones.” He’s a lawyer, a painter and the editor of a puzzle column in a popular Israeli newspaper.
F
The mystery of REM sleep is that even though it may not be essential, it is ubiquitous – at least in mammals and birds. But that doesn’t mean all mammals and birds dream (or if they do, they’re certainly not – talking about it). Some researchers think REM may have evolved for physiological reasons. “One thing that’s unique about mammals and birds is that they regulate body temperature”, says neuroscientist Jerry Siegel, director of UCLA’s Center for Sleep Research. “There’s no good evidence that any coldblooded animal has REM sleep.” REM sleep heats up the brain and non-REM cools it off, Siegel says, and that could mean that the changing sleep cycles allow the brain to repair itself. “It seems likely that REM sleep is filling a basic physiological function and that dreams are a kind of epiphenomenon,” Siegel says – an extraneous byproduct; like foam on beer.
G
Whatever the function of dreams at night, they clearly can play a role in therapy during the day. The University of Maryland’s Clara Hill, who has studied the use of dreams in therapy, says that dreams are a ‘backdoor’, into a patient’s thinking. “Dreams reveal stuff about you that you didn’t know was there,” she says. The therapists she trains to work with patients’ dreams are, in essence, heirs to Freud, using dream imagery to uncover hidden emotions and feelings. Dreams provide clues to the nature of the more serious mental illness. Schizophrenics, for example, have poor-quality dreams, usually about objects rather than people. “If you’re going to understand human behavior,” says Rosalind Cartwright, a chairman of psychology at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, “here’s a big piece of it. Dreaming is our own storytelling time – to help us know who we are, where we’re going and how we’re going to get there.” Cartwright has been studying depression in divorced men and women, and she is finding that “good dreamers,” people who have vivid dreams with strong storylines, are less likely to remain depressed. She thinks that dreaming helps diffuse strong emotions. “Dreaming is a mental-health activity,” she says.
Questions 1-5
Reading Passage has seven paragraphs, A-G.
Which paragraph contains the following information?
Write the correct number, A-G, in boxes 1-5 on your answer sheet.
1 ABCDEFG Reference of an artist’s dreams who has versatile talents
2 ABCDEFG The dream actually happens to many animals
3 ABCDEFG Dreams are related to benefit and happiness
4 ABCDEFG advanced scientific technology applied in the investigation of the REM stage.
5 ABCDEFG questioning concern raised about the usefulness of investigation on dreams
Questions 6-8
Choose the correct letter, A, B, C or D.
Write your answers in boxes 6-8 on your answer sheet.
6. What were dreams regarded as by ancient people?
A superstitious and unreliable
B communication with gods and chance to predict the future
C medical relief for children with an ill desire
D rules to follow as they fell asleep in a temple
7. According to Paragraph D, which part of the brain controls reasoning?
A anterior cingulate cortex
B internal cortex
C limbic system
D prefrontal cortex
8. What can we conclude when the author cited a reference for dreams in animals?
A Brain temperature rises when REM pattern happens.
B The reason why mammals are warm-blooded
C mammals are bound to appear with more frequent REM.
D REM makes people want to drink beer with more foam.
Questions 9-14
Look at the following people and the list of statements below.
Match each statement with the correct person, A-G.
Write the correct letter, A-G, in boxes 9-14 on your answer sheet.
List of people
A Sigmund Freud
B Allan Hobson (Harvard)
C Robert McCarley
D Eric Nofzinger
E Jerry Siegel
F Clara Hill
G Rosalind Cartwright
9 ABCDEFG Dreams sometimes come along with REM as no more than a trivial attachment
10 ABCDEFG Exploring patients’ dreams would be beneficial for treatment as it reveals the unconscious thinking
11 ABCDEFG Dreams help people cope with the difficulties they meet in the daytime
12 ABCDEFG Decoding dreams would provide a reminder to human desire in the early days
13 ABCDEFG Dreams are a body function to control strong emotion
14 ABCDEFG Dreams seem to be as randomly occurring and have limited research significance.








